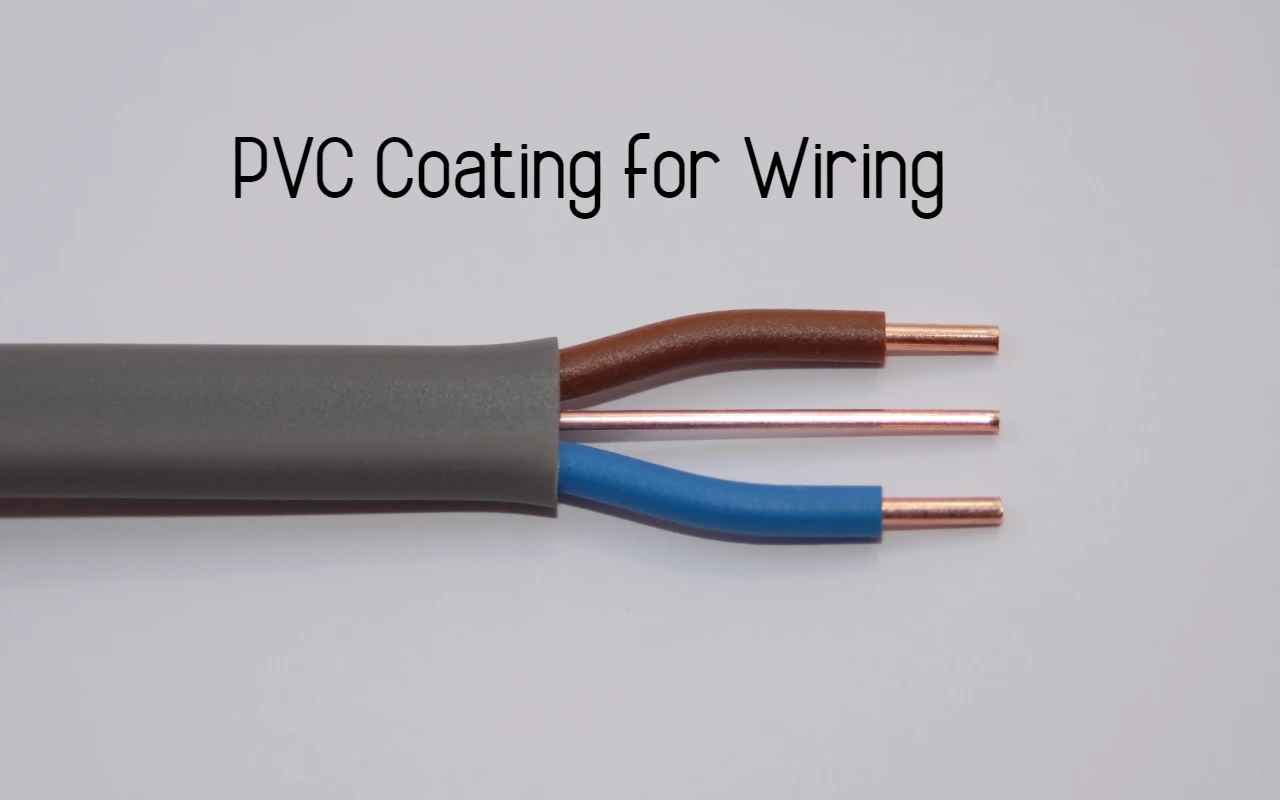
Why are Electric Wires Coated with PVC

Electric wires are coated with PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) for several important reasons. Here’s why PVC is commonly used as a coating material for electric wires:
- Insulation: The primary function of the PVC coating on electric wires is to provide insulation. PVC has excellent electrical insulation properties, preventing the flow of electric current between conductors and reducing the risk of electrical shocks or short circuits. The PVC coating helps to maintain the integrity and safety of the electrical system.
- Protection: PVC provides a protective barrier for the underlying conductors. It shields the wires from external factors such as moisture, chemicals, abrasion, and mechanical damage. The PVC coating acts as a physical barrier, safeguarding the wires and extending their lifespan.
- Fire Resistance: PVC is inherently fire-resistant, which is crucial for electrical wiring applications. It has a high ignition temperature and low flammability, making it a suitable choice for minimizing fire hazards. PVC-coated wires help prevent the spread of fire in case of electrical faults or overheating.
- Durability: PVC is a durable material that can withstand various environmental conditions. It is resistant to moisture, sunlight, and many chemicals, ensuring that the wire remains reliable and functional over an extended period. The PVC coating helps protect the wire from degradation and maintains its performance.
- Flexibility: PVC-coated wires exhibit flexibility, which facilitates easy installation and routing in various applications. The flexibility of the PVC coating allows the wires to be bent and maneuvered without cracking or breaking, ensuring ease of use during installation.
- Cost-effectiveness: PVC is a cost-effective material, making it a popular choice for wire coating. It offers a balance between performance and affordability, making it suitable for a wide range of residential, commercial, and industrial wiring applications.
In summary, PVC is used to coat electric wires primarily for insulation, protection, fire resistance, durability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. The PVC coating ensures the safety, longevity, and reliable performance of the wires in various electrical systems.
Importance of Coating Electric Wires With PVC

Coating electric wires with PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is of utmost importance due to the following reasons:
- Electrical Insulation: One of the primary purposes of PVC coating on electric wires is to provide electrical insulation. PVC is an excellent insulating material that prevents the flow of electric current between conductors. It acts as a protective layer, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and short circuits. Insulated wires are crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient transmission of electricity.
- Safety: PVC-coated wires enhance the safety of electrical systems. By insulating the conductors, the PVC coating minimizes the chances of accidental contact with live wires, reducing the risk of electrical accidents, fires, and injuries. It provides a barrier between the electric current and the surrounding environment, preventing electrical hazards.
- Environmental Protection: PVC coating helps protect electric wires from environmental factors such as moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. Moisture can cause short circuits and damage to the wires, while chemicals and abrasion can deteriorate their performance. PVC acts as a barrier, safeguarding the wires from these detrimental elements, thereby extending their lifespan and ensuring reliable operation.
- Fire Resistance: PVC is inherently fire-resistant, making it an essential coating material for electric wires. In the event of an electrical fault or overheating, the PVC coating inhibits the spread of fire, limiting its impact and providing valuable time for mitigation and evacuation. Fire-resistant PVC-coated wires contribute to fire safety in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
- Durability and Longevity: The PVC coating enhances the durability of electric wires, enabling them to withstand various environmental conditions and mechanical stresses. PVC-coated wires are resistant to moisture, sunlight, chemicals, and physical damage. This durability ensures that the wires maintain their performance over an extended period, reducing the need for frequent replacements and minimizing downtime.
- Easy Installation: PVC coating makes electric wires flexible and easy to handle during installation. The flexibility allows for easy routing and bending around corners, making it convenient for electricians to install the wiring in different locations and structures. The ease of installation saves time and effort, improving overall efficiency.
In summary, coating electric wires with PVC is vital for electrical insulation, safety, environmental protection, fire resistance, durability, and easy installation. PVC-coated wires provide reliable and efficient electrical transmission while minimizing the risk of electrical hazards, ensuring the longevity and integrity of electrical systems.
Properties and Advantages of PVC as A Wire Coating Material

PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride) is a widely used material for coating wires due to its numerous properties and advantages. Here are some key properties and advantages of PVC as a wire coating material:
- Electrical Insulation: PVC is an excellent electrical insulator. It effectively prevents the flow of electric current between conductors, reducing the risk of electrical shocks and short circuits. PVC-coated wires provide a reliable insulation layer that ensures the safe and efficient transmission of electricity.
- Chemical Resistance: PVC exhibits excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, oils, and solvents. This chemical resistance makes PVC-coated wires suitable for applications where exposure to corrosive or aggressive substances is possible, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the wires.
- Thermal Stability: PVC has good thermal stability, allowing it to withstand a wide range of temperatures without deformation or degradation. PVC-coated wires can handle both high and low temperature environments, making them suitable for various applications, including both indoor and outdoor installations.
- Flexibility: PVC-coated wires offer flexibility, which facilitates easy installation and routing in different applications. The flexibility of PVC allows the wires to be bent, twisted, and maneuvered without cracking or breaking. This flexibility ensures convenient installation, even in complex wiring setups.
- Mechanical Strength: PVC provides mechanical strength and durability to wires. It offers resistance against abrasion, impact, and physical stresses. PVC-coated wires can withstand bending, pulling, and other mechanical forces encountered during installation and everyday use, ensuring their long-term performance and reliability.
- Moisture Resistance: PVC is inherently moisture-resistant, providing protection against water and moisture ingress. PVC-coated wires are less susceptible to damage caused by moisture, which can lead to electrical malfunctions and corrosion. This moisture resistance enhances the lifespan and performance of the wires, particularly in humid environments.
- Cost-effectiveness: PVC is a cost-effective wire coating material. It is relatively inexpensive compared to other coating materials, such as rubber or silicone. This cost-effectiveness makes PVC-coated wires a popular choice for a wide range of applications where electrical insulation and protection are required without breaking the budget.
In summary, PVC offers properties such as electrical insulation, chemical resistance, thermal stability, flexibility, mechanical strength, moisture resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it an advantageous choice for wire coating. PVC-coated wires provide reliable insulation, protection, and durability in various electrical and wiring applications.
Application Areas For PVC-Coated Electric Wires

PVC-coated electric wires find wide application in various industries and settings due to their versatile properties and advantages. Here are some common application areas for PVC-coated electric wires:
- Residential Wiring: PVC-coated wires are extensively used in residential wiring applications, including the wiring of outlets, switches, lighting fixtures, and appliances. They provide reliable electrical insulation, flexibility, and durability, ensuring safe and efficient electrical distribution within homes.
- Commercial Buildings: PVC-coated wires are suitable for commercial building wiring, including offices, retail spaces, schools, hospitals, and hotels. They are used for powering electrical devices, lighting systems, HVAC systems, and other electrical equipment. The PVC coating protects the wires from environmental factors, ensuring long-term performance.
- Industrial Installations: PVC-coated wires are employed in various industrial installations and facilities, such as manufacturing plants, warehouses, and industrial machinery. They are used for power transmission, control systems, motor connections, and equipment wiring. The PVC coating offers chemical resistance, mechanical strength, and insulation in demanding industrial environments.
- Automotive Wiring: PVC-coated wires are widely utilized in automotive applications, including wiring harnesses, vehicle lighting, and electrical systems. They can withstand temperature variations, vibrations, and exposure to oils, fuels, and chemicals commonly found in automotive environments.
- Construction Projects: PVC-coated wires are commonly used in construction projects, both residential and commercial. They are employed for temporary electrical installations, such as construction site power distribution, lighting, and machinery connections. PVC coating provides protection against physical damage during construction activities.
- Outdoor Applications: PVC-coated wires are suitable for outdoor applications, such as landscape lighting, outdoor signage, and underground electrical installations. The PVC coating offers excellent weather resistance, UV resistance, and moisture protection, ensuring the wires withstand outdoor conditions.
- Appliances and Electronics: PVC-coated wires are used in the manufacturing of appliances, electronics, and electrical devices. They are employed in the internal wiring of refrigerators, washing machines, televisions, computers, and other consumer electronics, providing insulation and electrical conductivity.
In summary, PVC-coated electric wires have broad application areas, including residential wiring, commercial buildings, industrial installations, automotive wiring, construction projects, outdoor applications, and appliances/electronics. The PVC coating provides insulation, protection, and durability, making these wires suitable for various electrical and wiring needs in different industries and settings.
Maintenance and Care For PVC-Coated Electric Wires
Maintaining and caring for PVC-coated electric wires is important to ensure their longevity, safety, and optimal performance. Here are some maintenance and care tips for PVC-coated electric wires:
- Regular Inspection: Conduct periodic visual inspections of the PVC-coated wires to check for any signs of damage, such as cracks, cuts, or exposed conductors. If any issues are detected, promptly replace or repair the affected section to prevent further damage or electrical hazards.
- Cleaning: Keep the PVC-coated wires clean and free from dust, dirt, or debris. Regularly wipe down the wires using a dry or slightly damp cloth to remove any accumulated dirt. Avoid using harsh chemicals or solvents, as they may damage the PVC coating.
- Avoid Excessive Heat: PVC-coated wires have temperature limits specified by the manufacturer. Ensure that the wires are not exposed to temperatures beyond their recommended range. Excessive heat can cause the PVC coating to degrade or melt, compromising the insulation and leading to electrical faults.
- Protection from Physical Damage: Take precautions to protect PVC-coated wires from physical damage. Avoid sharp objects, heavy impacts, or excessive bending or twisting that may cause the PVC coating to crack or peel. Properly route and secure the wires to prevent them from being snagged, pinched, or pulled.
- Moisture Protection: PVC-coated wires offer moisture resistance, but it’s still important to prevent prolonged exposure to excessive moisture or water. Ensure that the wires are installed in areas with proper waterproofing measures, and avoid submerging them in water or exposing them to high humidity environments.
- Handling with Care: When working with PVC-coated wires during installations, handle them with care to avoid unnecessary stress or strain. Use appropriate tools and techniques for cutting, stripping, and terminating the wires to prevent damage to the PVC coating or underlying conductors.
- Professional Maintenance: In cases where the wiring system requires maintenance or repairs, it’s advisable to consult a professional electrician. They have the expertise to handle any issues related to PVC-coated wires and ensure compliance with safety standards.
By following these maintenance and care guidelines, you can help prolong the lifespan and ensure the safe operation of PVC-coated electric wires. Regular inspections, cleanliness, protection from physical damage, temperature control, and professional assistance when needed will contribute to the optimal performance and reliability of the wiring system.
Manufacturing Process of PVC-Coated Electric Wires
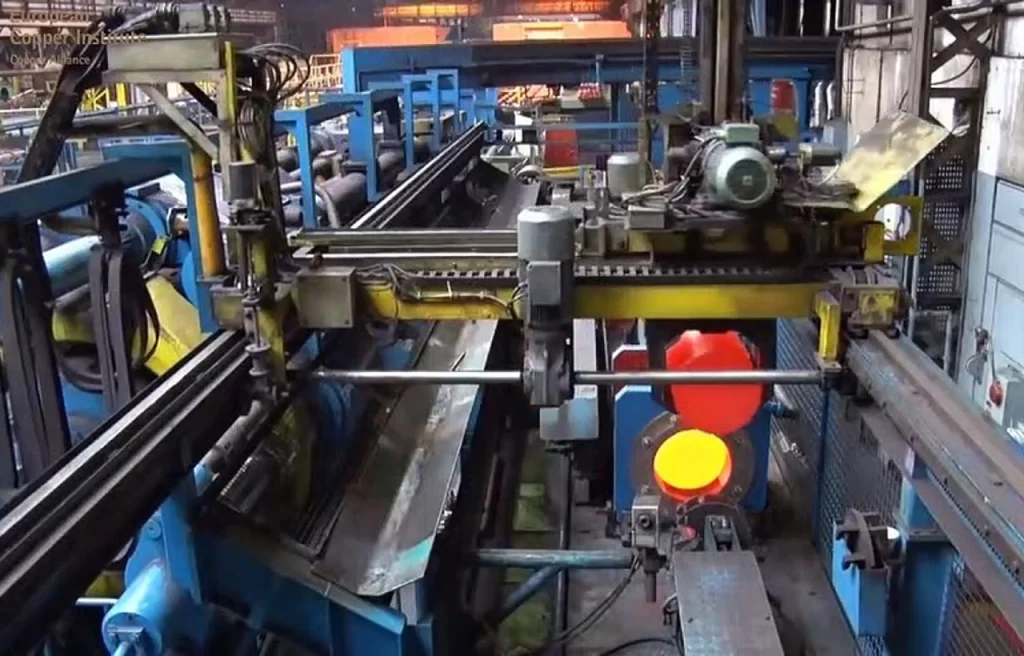

The manufacturing process of PVC-coated electric wires involves several steps to create the final product. Here’s an overview of the typical manufacturing process:
- Wire Drawing: The process begins with wire drawing, where copper or aluminum rods are drawn through a series of dies to reduce their diameter to the desired size. This step ensures that the wire has the required conductivity and strength.
- Annealing: The drawn wire is then subjected to annealing, a heat treatment process that helps to soften the wire and improve its flexibility and ductility. Annealing also relieves any stresses induced during the wire drawing process.
- Cleaning and Preparing the Wire: The wire is cleaned thoroughly to remove any dirt, oils, or residues that may hinder adhesion between the PVC coating and the wire surface. This step is important to ensure a strong bond between the wire and the PVC coating.
- PVC Coating Extrusion: The cleaned wire is passed through an extrusion machine, where PVC material in the form of pellets or powder is melted and forced through a die. The die imparts the desired shape and size to the PVC coating, which is applied uniformly around the wire. The extruded wire is then cooled rapidly to solidify the PVC coating.
- Cooling and Curing: After the PVC wire is applied, the wire is passed through a cooling chamber to ensure proper solidification of the PVC material. Subsequently, the wire is exposed to heat for a specific duration to complete the curing process. This step enhances the PVC’s properties and ensures it attains its desired strength and durability.
- Inspection and Testing: The PVC-coated wires undergo rigorous inspection and testing to ensure they meet quality standards. Tests may include checking the PVC coating thickness, adhesion strength, electrical conductivity, and other relevant parameters. Any defective wires are identified and removed from the production line.
- Spooling and Packaging: Once the PVC wires pass inspection, they are wound onto spools or reels for easy handling, storage, and transportation. The wires are then packaged securely to protect them from damage during transit.
It’s important to note that specific manufacturing processes may vary based on factors such as wire gauge, coating thickness, and industry standards. Additionally, manufacturers adhere to safety and quality regulations to produce PVC-coated electric wires that meet the required electrical and performance specifications.
Types of PVC Coatings Used in Electric Wires
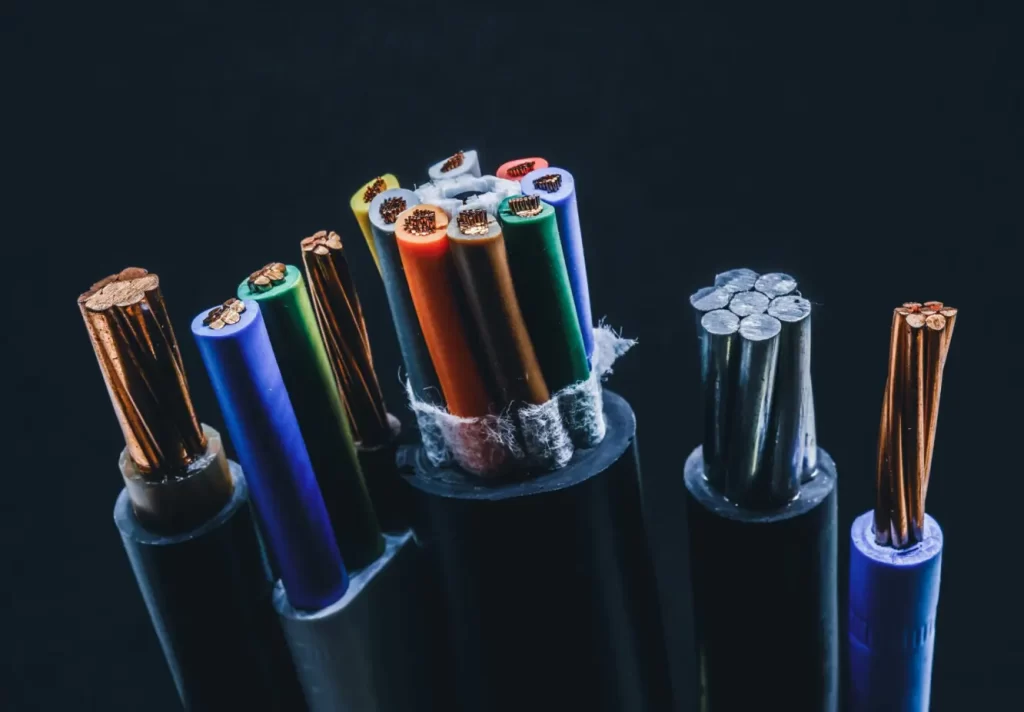

There are different types of PVC coatings used in electric wires, each designed to meet specific requirements and applications. Here are some common types of PVC coatings used in electric wires:
- General-Purpose PVC: This is the most commonly used PVC coating for electric wires. It offers good electrical insulation properties and protection against moisture, chemicals, and abrasion. General-purpose PVC coatings provide a balance between cost-effectiveness and performance, making them suitable for a wide range of applications in residential, commercial, and industrial settings.
- Flame-Retardant PVC: Flame-retardant PVC coatings are specifically formulated to inhibit the spread of fire. These coatings contain additives that enhance their fire resistance properties, reducing the risk of the wire contributing to a fire. Flame-retardant PVC-coated wires are commonly used in buildings, automotive applications, and other areas where fire safety is a concern.
- Low-Smoke and Halogen-Free PVC: Low-smoke and halogen-free PVC coatings are designed to minimize the emission of toxic gases and smoke in the event of a fire. These coatings contain additives that reduce the release of harmful substances, making them suitable for applications where human safety and environmental concerns are important, such as public spaces, transportation, and data centers.
- UV-Resistant PVC: UV-resistant PVC wire are used in wires intended for outdoor applications or areas exposed to direct sunlight. These coatings incorporate stabilizers that protect the wire from the degrading effects of UV radiation, preventing the PVC from becoming brittle or discolored over time. UV-resistant PVC coatings ensure the long-term performance and durability of wires in outdoor installations.
- Oil and Chemical Resistant PVC: PVC Coated for Wires used in industrial settings or environments where exposure to oils, solvents, and chemicals is common may have PVC wire with enhanced resistance to these substances. Oil and chemical resistant PVC coatings provide a protective barrier that prevents the corrosive effects of these substances, ensuring the longevity and reliability of the wires.
- High-Temperature PVC: High-temperature PVC coatings are designed to withstand elevated temperatures without deforming or melting. These coatings are used in wires that are subjected to high-temperature environments, such as ovens, furnaces, and automotive engine compartments. High-temperature PVC wire maintain their electrical insulation properties and structural integrity under demanding thermal conditions.
These are just a few examples of the different types of PVC coatings used in electric wires. The selection of the PVC coating depends on the specific requirements of the application, including electrical insulation, environmental conditions, fire safety regulations, and chemical resistance. Manufacturers offer a variety of PVC coatings to meet diverse needs and ensure the reliable and safe operation of electrical systems.
Electrical Conductivity of PVC-Coated Wires
PVC-coated wires are primarily used for their electrical insulation properties rather than their electrical conductivity. PVC, or polyvinyl chloride, is a non-conductive material, meaning it does not conduct electricity. When PVC for wiring is used as a coating for wires, its main function is to provide insulation and protection to the underlying conductive material, typically copper or aluminum.
The conductive core of the wire, such as copper or aluminum, carries the electrical current. The PVC coating acts as a barrier, preventing contact between the conductive core and external objects or materials. This insulation helps to minimize the risk of electrical shocks, short circuits, and other electrical hazards.
While PVC itself is not conductive, it is important to note that the thickness of the PVC coating can have an impact on the overall electrical performance of the wire. Thicker PVC coatings may introduce a small increase in resistance due to their insulating nature. However, for most standard applications, the impact on electrical conductivity is negligible and does not significantly affect the overall performance of the wire.
It’s worth mentioning that the conductive core of the wire, whether copper or aluminum, provides the desired electrical conductivity. These metals are known for their excellent electrical conductivity properties, making them ideal choices for conducting electricity efficiently within the wire.
In summary, PVC-coated wires are not selected for their electrical conductivity but rather for their insulation properties. The PVC coating ensures the safe transmission of electricity by providing electrical insulation and protection to the conductive core of the wire, allowing for reliable and efficient electrical performance.
Role of PVC coatings in preventing electrical accidents and hazards
PVC coatings play a crucial role in preventing electrical accidents and hazards by providing insulation and protection to wires. Here are the key roles of PVC coatings in electrical safety:
- Electrical Insulation: PVC coatings act as effective electrical insulators, preventing the flow of electricity from the conductive core of the wire to external objects or materials. This insulation helps to avoid electrical shocks and reduces the risk of accidental contact with live wires, enhancing overall electrical safety.
- Voltage Resistance: PVC coatings have high voltage resistance, allowing them to withstand the electrical potential difference present in electrical systems. By preventing voltage leakage or short circuits, PVC coatings help maintain the integrity and reliability of electrical circuits, reducing the risk of electrical accidents and fires.
- Protection from Moisture and Chemicals: PVC wire offer excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and environmental factors. They act as a barrier, preventing water, moisture, or chemicals from coming into direct contact with the conductive core of the wire. This protection safeguards against corrosion, degradation, and short circuits that could result from exposure to moisture or corrosive substances.
- Mechanical Protection: PVC wire coatings provide mechanical protection to the underlying conductive wires. They offer resistance against abrasion, impact, and physical damage, helping to maintain the structural integrity of the wires. This protection ensures that the wires remain intact and do not get damaged during installation, use, or maintenance, minimizing the risk of electrical faults.
- Thermal Insulation: PVC coated wire have thermal insulation properties, helping to mitigate the risk of heat transfer and excessive temperature rise in electrical systems. They act as a barrier that reduces the chances of overheating, melting, or fire outbreaks due to electrical faults or short circuits.
- Flame Retardancy: PVC coated wire can be formulated to exhibit flame retardant properties. This means they are designed to resist the spread of fire and emit minimal smoke and toxic gases when exposed to high temperatures. Flame retardant PVC wire help to prevent or delay the propagation of fires caused by electrical faults, reducing the potential for damage and enhancing occupant safety.
By providing electrical insulation, voltage resistance, protection from moisture and chemicals, mechanical protection, thermal insulation, and flame retardancy, PVC wire significantly contributes to preventing electrical accidents and hazards. They ensure the safe transmission of electricity, minimize the risk of electrical shocks, fires, and equipment damage, and promote overall electrical system safety.


Leave a Reply